
How to Become a Space Scientist
To become a space scientist, you should start with a strong foundation in science and math, pursue a relevant bachelor's degree, and then advance to a master's or Ph.D.
Request Information
For every single person who set foot on the moon, there are thousands of people behind the scenes who engineered the rockets that got them up there," said Curt Hanson, head of UND's special collections. Without these individuals, so much wouldn't have been possible, including the historic moon landing. John Disher, a University of North Dakota (UND) graduate, was key to achieving President Kennedy's goal of landing on the moon by the end of the 1960s through his assessment of NASA's timeline.
If you're captivated by the stars or intrigued by the technology that gets us there, a career in space science might be your calling. But, how to become a space scientist? Well, it all starts with understanding the steps—so let's see what it takes to turn you from a curious stargazer into an expert.
How to Become a Space Scientist
To become a space scientist, one needs to have a strong sense of curiosity as well as a love for exploring the unknown. Vincent Ledvina, a UND student, recalls, "Even at age 4, I knew what the Aurora was and what the Northern Lights were." Such childhood fascination and wonder can often guide a person throughout their career aspirations.
However, turning that dream into reality requires much more than mere passion. It takes careful planning, education, and experience in order to become a space scientist.
Step 1: Develop a strong foundation in science and math
Firstly, reading and learning more about space exploration can help determine your career aspirations. This is true for those set on becoming space scientists or those simply curious about what lies beyond our planet.
Studies show that space exploration has a significant impact on inspiring young people to pursue careers in math and science. Actually, over 39% of respondents in a survey strongly agree that space exploration encourages students to study these important subjects.
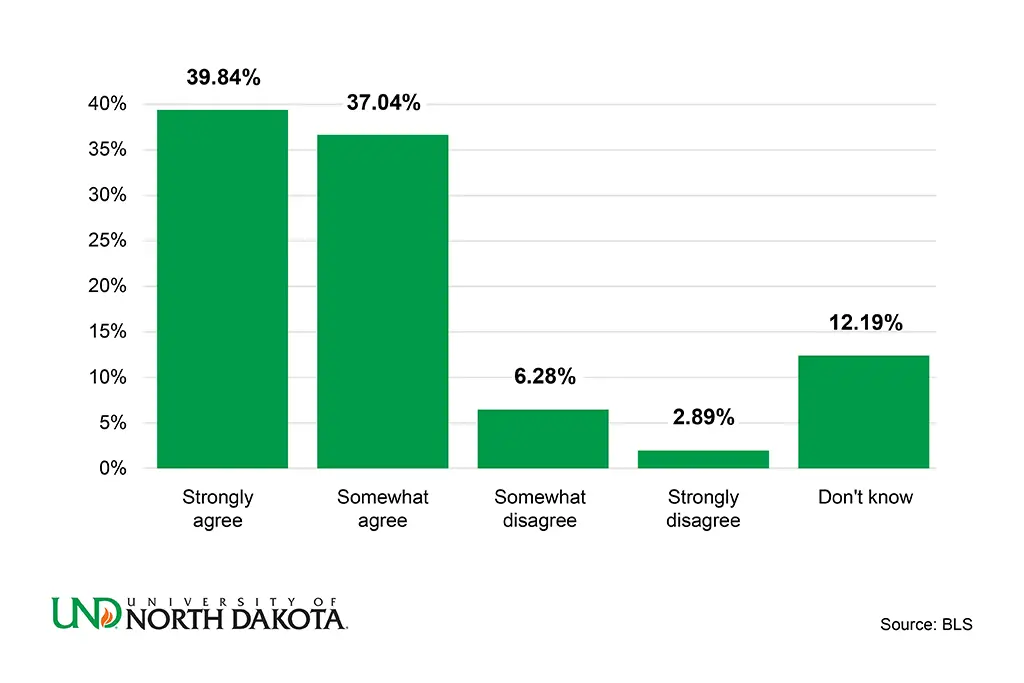
Building foundational knowledge in science-related subjects early on is important for a field as impactful as space science. So, the key is to focus on subjects like physics, chemistry, and advanced math. They are the basis for understanding how the universe works.
Step 2: Earn a relevant bachelor's degree
After high school, the next step is to pursue a bachelor's degree. Some common choices include physics, astronomy, aerospace engineering, planetary science, and other relevant fields. This is also a great time to get involved in research projects or internships.
UND offers many opportunities for undergraduate and graduate students pursuing space science to partake in projects and internships. Through programs like the North Dakota Space Grant Consortium (NDSGC), students can participate in NASA-relevant research while working closely with faculty mentors. These research fellowships allow students to explore various space science topics, from studying solar flares to developing space exploration tools.
Additionally, UND's Human Spaceflight Laboratory provides students with unique opportunities to work on real space missions, such as testing space suits and living in an Inflatable Lunar Habitat.
Step 3: Pursue advanced degrees
To really make your mark in space science, you'll also need to pursue advanced degrees. At this level, you have even more opportunities to conduct original research, work with cutting-edge technology, and collaborate with experts in the field.

UND graduates with M.S. in Space Studies or Ph.D. in Aerospace Sciences have achieved remarkable success in their careers. They have secured positions at top space exploration enterprises and leading aerospace technology firms.
In fact, UND was the first university with a NASA-funded lab dedicated to designing space exploration suits and planetary surface exploration gear. The university also boasts two fully operational space flight simulators and offers one of the few human spaceflight training programs available at a university.
A great example of the opportunities provided by UND's Space Studies program is Stefan Tomovic, a 2021 graduate. While earning his master's degree, Tomovic participated in two research studies in UND's Inflatable Lunar/Mars Habitat. Today, he works at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, contributing to groundbreaking space missions.
An advanced degree, especially one in a university that is equipped with the right tools to help you advance, is necessary if you want more than just to secure a job position. With such a qualification, you'll be contributing to the industry's future.
Step 4: Gain experience
It's worth reiterating that experience is indispensable for aspiring space scientists. So, even after graduating, prioritize gaining experience and advancing through what you learn directly from the industry.
You can look for jobs, internships, research assistantships, or cooperative programs with space agencies like NASA, universities, or private space companies. UND's ties to such organizations provide students with unparalleled opportunities to engage with the forefront of the space industry.
Additionally, attending conferences and networking events can also help you build relationships with others in the field. The important thing is to have a means of applying what you've learned in real-world settings and connecting with professionals who can guide your career.
Building the Necessary Skills for a Space Science Career
Space scientists must have a thorough comprehension of the technical and non-technical abilities needed for their roles.
Without the necessary soft skills, they could have trouble collaborating with others, as well as might misinterpret or fail to convey critical findings. Thus, the lack of soft skills could jeopardize the mission objectives. Similarly, without technical expertise, they wouldn't even be able to process the amounts of data the rovers collect, resulting in missed opportunities for groundbreaking discoveries.
Technical skills: Mastering the tools of the trade
Some of the technical skills necessary for space scientists include:
- Data analysis
- Programming
- Engineering design
- Remote sensing and image processing
- Laboratory techniques
- Systems engineering
Additionally, considering the huge impact of machine learning and AI on all industries, space scientists can also benefit from being skilled in using these advanced tools and technologies. They can help ensure more accurate data analysis and predictions.

Developing soft skills: Beyond the technical
Space scientists also require soft skills, such as:
- Critical thinking
- Communication skills
- Teamwork
- Problem-solving
- Adaptability
- Time management
These skills are just as important as the technical expertise of space scientists. Just think about the International Space Station (ISS). The program is a collaborative effort that includes over 18 countries. In it, scientists and engineers work side by side to conduct research that would be impossible for any single nation to achieve alone.
In broader terms, the ISS symbolizes how space exploration pushes us to look beyond borders and work as a united global community. However, on a smaller scale, it also reminds us that successful space missions require people who can listen, collaborate, and build trust with one another.
Career Opportunities and Salaries in Space Science
Space science is a broad term that covers a range of disciplines related to the work performed to send vehicles into Earth's upper atmosphere or even further than that. Therefore, this field offers a universe of career opportunities. Some potential career paths include:
- Astrophysicist
- Space engineer
- Planetary scientist
- Space explorer
- Satellite technician
- Space researcher
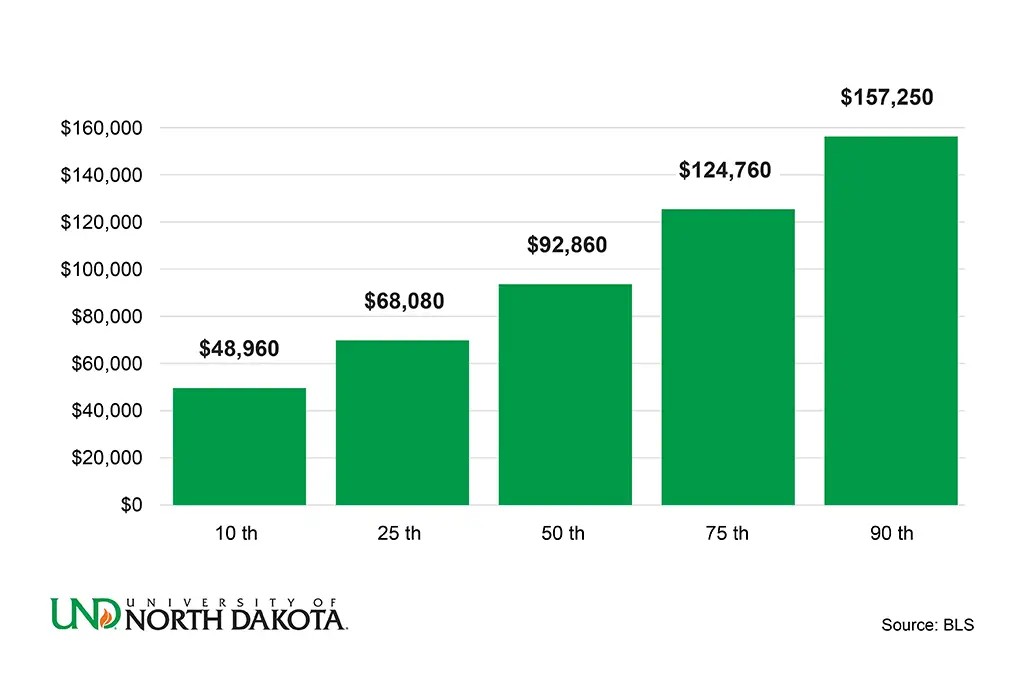
The exact salaries vary for each role. However, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports that the overall range of earnings for atmospheric and space scientists is as follows:
- 10th percentile: $48,960
- 25th percentile: $68,080
- 50th percentile (median): $92,860
- 75th percentile: $124,760
- 90th percentile: $157,250
These professionals can work in different industries. The ones with the highest levels of employment are:
- Federal, state, and local government (excluding state and local government schools and hospitals and the U.S. postal service)
- Other professional, scientific, and technical services
- Colleges, universities, and professional schools
- Radio and television broadcasting stations
- Scientific research and development services
Challenges and Rewards of Being a Space Scientist
As Neil deGrasse Tyson aptly puts it, "Scientists live at the boundary between what is known and unknown in the cosmos." If you pursue a career in this field, know that you'll be constantly facing uncertainty and returning to the drawing board. You have to do so not because something went wrong but because discovery is an ongoing process.
The emotional highs and lows of the profession are real. The challenge lies in embracing ignorance as the starting point for exploration. Yet, the rewards are immense. There's a deep sense of accomplishment in pushing the boundaries of human understanding, in being part of something bigger than oneself.
Stefan Tomovic puts it beautifully: "I feel what I do at work has a positive impact for humanity. That's one of the most rewarding things about the job: knowing that what I help research and development has the potential to shape the future and also make our life here on Earth better." This sense of purpose—contributing to something greater than oneself, makes any setbacks worthwhile.
The Future of Space Science
The future of space science is filled with possibilities. The global space economy, which is already valued at over $423.8 billion in 2019, is poised to expand even more. This is largely thanks to satellite technology and space-based internet infrastructure as they continue to evolve.
Experts predict that communications activities will make up more than 50% of the space economy by 2040. Meanwhile, innovations in space agriculture, like UND's Space Ag Conference and Interstellar Lab's BioPods, are setting the stage for something even bigger: sustainability in space.
As NASA's Ralph Fritsche calls it, we're in a "golden era" of space research, where the focus is shifting from merely reaching new worlds to actually solving the challenges of living there. As we advance, collaboration between public and private sectors will be key in tackling these challenges, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in space science.
UND's contributions, particularly through its Inflatable Lunar-Mars Habitat research, are an excellent example of how combining agriculture with space studies could one day sustain human life beyond Earth.
So, to put it simply, the future of space exploration is all about ensuring that humanity thrives once we get there.
Conclusion
The behind-the-scenes work that goes into space missions is what truly defines their success. As Hanson said, "It's natural that the people who actually set foot on the moon get most of the attention, but without people like John Disher, there's no Neil Armstrong."
Are you ready for liftoff? If so, join UND's Department of Space Studies to learn about the mysteries of the universe and gain the skills needed to explore them yourself. With cutting-edge technology, research opportunities, innovative projects, and a community of like-minded explorers, UND offers the perfect environment for all those interested in turning their passion for space into a successful and meaningful career.
FAQs
Certainly! A space science degree is an excellent choice for those passionate about space exploration, offering diverse career opportunities in space agencies and related industries.
To become a NASA scientist, you need advanced degrees in a relevant field and substantial experience. Specific requirements vary depending on the position you apply for, but research and internships are essential steps.