Transcripts
Transcripts provide an accurate text version of audio content, either for video or audio files.
Transcripts are usually formatted as a downloadable document, most commonly in Word format.
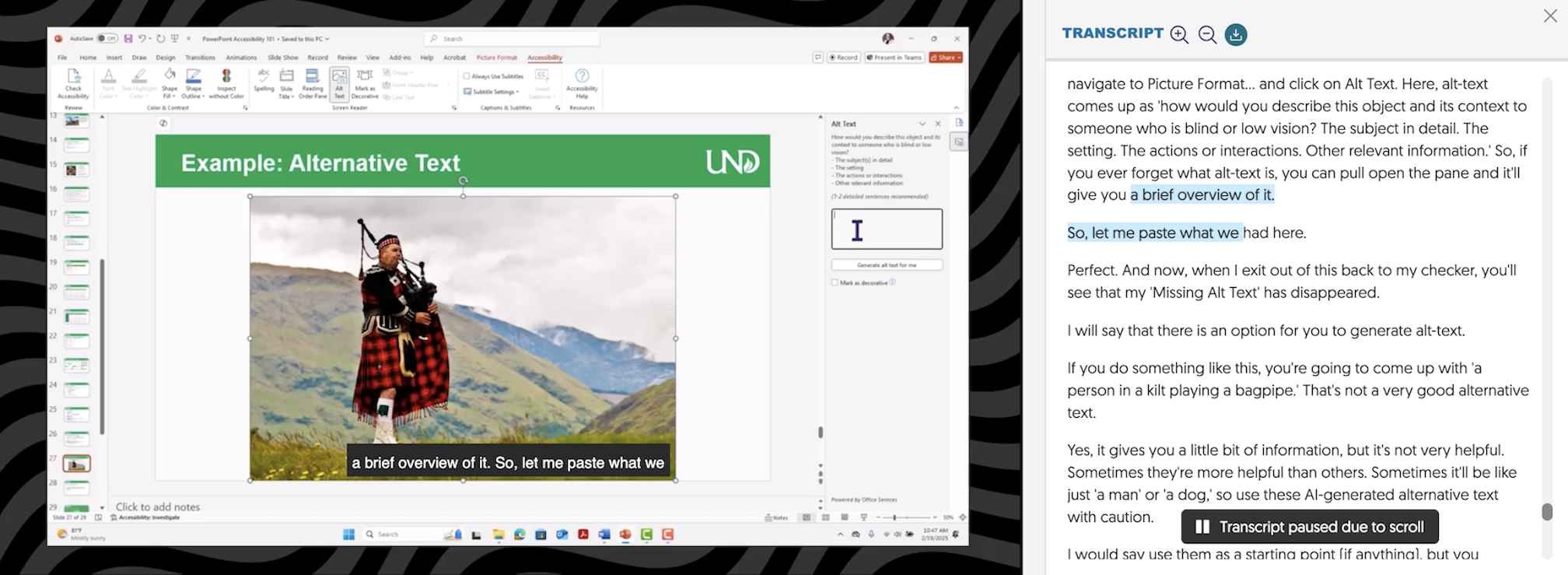
Transcript Example
Difference Between Audio and Video Transcripts
Audio Transcripts
A transcript is the only method of providing a text alternative for audio-only files. This can either be a downloadable document or text can be displayed alongside the audio file.
When audio files are embedded in another document, such as a PowerPoint file, a separate transcript is still needed.
Video Transcripts
Transcripts differ from captions in that the text is not displayed in sync with the video. Oftentimes, a transcript is viewed separately from its video file. Given this separation, transcripts need to include logical formatting (including headings). Transcripts also need to make sense on their own.
To provide an equitable experience of videos, synchronized captions are required; on their own, transcripts are not usually sufficient. However, there are cases where transcripts may be preferred or required. Having both available is recommended.
Who Benefits from Transcripts?
Transcripts can benefit deaf or hard-of-hearing users. They can also support many other learning strategies, including:
- Locating a specific point in a video
- Note-taking
- Learning new vocabulary
- Learning a new language
- Focusing
- Reviewing
- Searching for terms
Guidelines for Effective Transcripts
Consider the following guidelines when generating transcripts for audio and video files:
- Textually describe the scene.
- Include relevant, non-speech sounds (e.g., laughter, applause, or background noise), as these elements are essential for a complete understanding of the content.
- Decide if you want a verbatim or edited transcript
- Verbatim Transcript: includes all sounds, including stutters, pauses, and filler words (e.g., “hmmm” or “erm”).
- Edited Transcript: cleaned-up versions prioritizing grammar and punctuation, while maintaining the original context.
- Add labels or names to differentiate between multiple speakers. This organizes the transcript, making it easier to follow.
- Review your completed transcript for accuracy and correct any errors.
- Break the content down into defined sections and topics to make it easier for readers to navigate and comprehend.
- Link the transcript file to its accompanying audio or video.
Automatically Generated Transcripts
Automatically generated transcripts rely on speech recognition software. The accuracy of transcription may vary based on several factors: program software, audio quality, speaker dialect, and content complexity. To ensure accuracy, some post-editing may be required.